
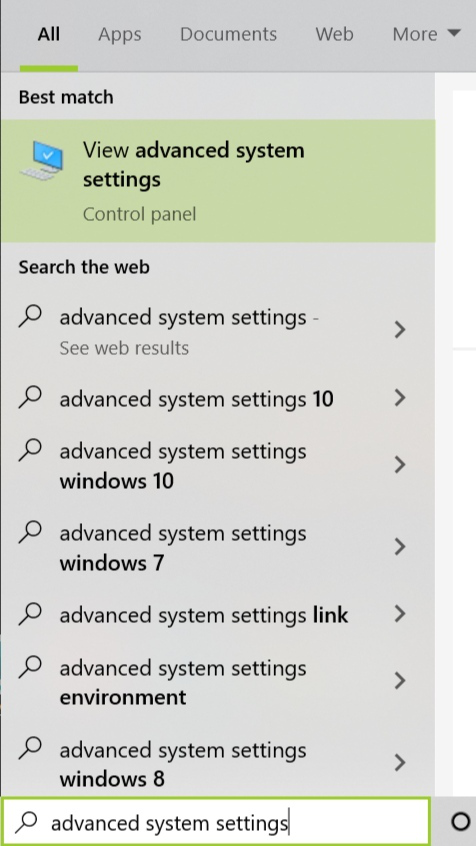

The above mentioned commands.Environment variables are stored in the. /Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0241.jdk/Contents/Home. Adding environment variableThis is the path where JDK is installed. In this post I will demonstrate how to set/unset and use environment variables.
Now bash usually requires you to restart the terminal to reflect the changes in bash_profile file. Bash_profile in the root directory vi ~/.bash_profileAnd add the following line to this file export USERNAME="jayesh"Where USERNAME is the key and jayesh is the value of this environment variable. Say, you want to add an environment variable for username, you can do it with following commands.First edit the. Every time you want to add new environment variable, you will make changes to this file.
Setting Environment Variable For Java Update The System
Bash_profile, refresh the system and then run printenv, it will still show the removed environment variable. As you will see if you remove the variables from. Removing environment variableEnvironment variable, once set they remain under system unless unset explicitly. Accessing environment variablesOnce you have this variable, you can access them in any shell script with following syntax, ENVThis will produce the value of jayesh in the script. ~/.bash_profileOnce this is done, you can view the list of all environment variables in the system by typing printenv on the terminal. This command will update the system with new environment variable.
Now, if you type printenv in the terminal you will see that variable is no longer in the list. ~/.bash_profile on the command line.Once this is done, run the following command in the terminal, unset USERNAMEThis will get completely rid of eliminated variable. Go to bash_profile file remove the line which sets the new variable and run.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
